You’ve just graduated, and the world of possibilities is open. Do you want to climb the corporate ladder, leading teams and making strategic decisions? Or do you see yourself diving deep into the world of finance, analyzing investments and managing risk? Both paths are exciting, and both require a strong foundation. This article explores the key differences between an MBA and a Masters in Finance vs MBA, helping you choose the degree that aligns with your career goals and passions.
Toc
Understanding the MBA: A Broad Business Perspective
An MBA, or Master of Business Administration, is not just a degree; it’s an opportunity to cultivate the skills and insights necessary to thrive in diverse business environments. This program is designed to produce well-rounded leaders who can navigate the complexities of various business functions. Within an MBA program, you’ll encounter a myriad of specializations such as marketing, operations, and finance, all aimed at providing a holistic view of the business landscape.
Pros and Cons of an MBA
Pros:
- Comprehensive Understanding: An MBA equips you with a broad understanding of business functions, making you adaptable in the job market.
- Leadership Preparation: With a focus on leadership, strategic thinking, and problem-solving, MBA graduates are often groomed for management roles across industries.
- Networking Opportunities: The robust alumni network associated with MBA programs can be invaluable for career advancement, connecting you with influential professionals in your field.
- Entrepreneurial Foundation: The diverse curriculum provides a solid foundation for those interested in launching their own ventures.
Cons:
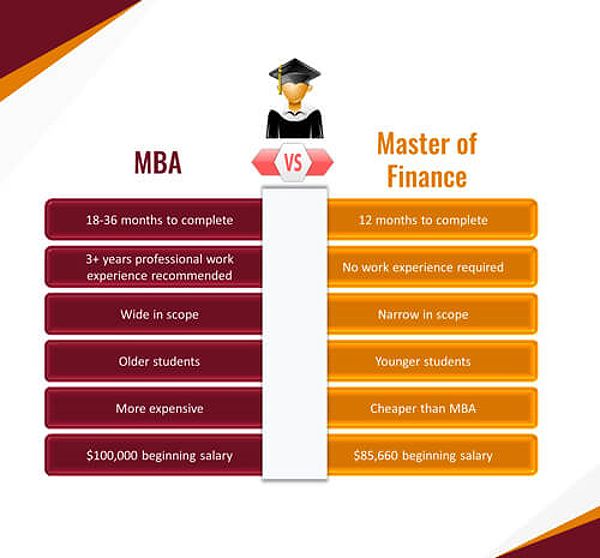
- Time and Cost: MBA programs typically span two years or more and can be more expensive than a master’s in finance, potentially leading to significant student debt.
- Work Experience Requirement: Many programs favor candidates with prior professional experience, which may not align with recent graduates’ timelines.
MBA Curriculum: A Comprehensive Approach
The curriculum of an MBA program is structured to cover a wide array of subjects. Core courses generally include accounting, finance, marketing, and operations management. Elective courses allow students to delve deeper into specific areas of interest, enhancing their expertise. Additionally, experiential learning through case studies and simulations offers practical experience, bridging the gap between theory and real-world application.

MBA Career Paths: Diverse and Rewarding
Graduates of MBA programs find themselves equipped for a plethora of career options. Whether your ambition is to become a management consultant, operations manager, marketing director, or even an entrepreneur, the versatility of the MBA prepares you for leadership roles across various industries. For instance, a friend of mine, after completing her MBA, landed a role as a product manager at a leading tech company, showcasing how this degree can open doors to exciting opportunities.
Comparing Masters in Finance vs MBA: A Deep Dive into Financial Expertise
In contrast to the MBA’s broad approach, a Master’s in Finance (MFin) offers a specialized focus on financial principles and practices. This degree is tailored for those looking to immerse themselves in the world of finance, emphasizing quantitative analysis, investment strategies, and risk management.
1. https://viralblogspost.com/mmoga-master-of-science-in-finance
2. https://viralblogspost.com/business-and-finance-degree
3. https://viralblogspost.com/mmoga-newtek-small-business-finance
4. https://viralblogspost.com/mmoga-wells-fargo-financing-home
5. https://viralblogspost.com/local-roofing-companies-that-finance
Pros and Cons of a Master’s in Finance
Pros:
- In-Depth Knowledge: An MFin program provides a deep understanding of financial theory and practice, preparing you for specialized roles in finance.
- Focused Career Preparation: Graduates are well-prepared for positions in investment banking, asset management, and corporate finance.
- Time and Cost Efficiency: MFin programs are often shorter and less expensive than MBA programs, making them appealing for those eager to start their careers.
- Foundation for Academia: The advanced knowledge gained can also serve as a strong foundation for those interested in financial research or academia.
Cons:
- Narrower Scope: The specialized nature of the MFin may limit exposure to other business disciplines and leadership training.
- Mathematical Rigor: Admission may require a strong background in mathematics and finance, which can be a hurdle for some candidates.
MFin Curriculum: A Focus on Finance
The curriculum of a Master’s in Finance is heavily centered around finance-related topics. Courses typically include financial analysis, investment management, risk assessment, and portfolio optimization. Students engage in advanced financial modeling and utilize industry-standard software to analyze data and forecast financial trends. The emphasis on research and practical applications enhances critical thinking skills, preparing graduates for the rigors of the finance sector.
MFin Career Paths: Specialized and Lucrative
Graduates with a Master’s in Finance often pursue specialized roles such as financial analysts, investment bankers, portfolio managers, and risk analysts. These positions are typically well-compensated, especially in financial hubs. A colleague of mine, who earned his MFin, secured a lucrative role as a financial analyst at a top investment firm, demonstrating the high demand for specialized finance professionals.
Making the Right Choice: Weighing Your Options
When contemplating the decision between an MBA or a Master’s in Finance, it’s crucial to weigh the trade-offs between breadth and specialization. Your choice should align with your career goals, interests, and financial situation.
Assessing Your Career Goals and Interests
Consider what type of role you envision for yourself. If you aspire to a general management position or a leadership role across various sectors, the MBA’s broad perspective may be more suitable. Conversely, if your passion lies strictly within finance, a Master’s in Finance could provide you with the specialized skills needed to excel in that domain.
Evaluating Financial Considerations
Financial implications play a significant role in your decision-making process. MBA programs can be costly and often require a longer commitment. Reflect on your budget and your willingness to incur student debt. On the other hand, a Master’s in Finance may be more cost-effective, allowing you to enter the job market sooner and start earning a salary.
Exploring Potential Earnings
Both MBA and Master’s in Finance graduates can enjoy lucrative career paths, but there are notable differences in earning potential. According to recent statistics, the median annual salary for financial managers, a common role for MBA graduates, was around $134,000 in 2021. In contrast, the median annual salary for financial analysts, a typical position for Master’s in Finance graduates, hovered around $81,000 during the same period. Keep in mind that these figures can vary significantly based on factors like location, industry, and individual experience.
Beyond the Degree: Building Your Skills and Network
Regardless of your choice between an MBA or a Master’s in Finance, developing soft skills such as communication, leadership, and teamwork will be essential for your success. Networking is equally important; engaging with professionals in your field can provide insights and opportunities that are not available in the classroom.
1. https://viralblogspost.com/mmoga-best-small-business-financing
2. https://viralblogspost.com/accounts-receivable-financing-factoring
3. https://viralblogspost.com/mortgage-financing-for-self-employed
Actionable Steps for Professional Growth
To enhance your career prospects, consider taking the following steps:
- Attend Industry Events: Networking with professionals can lead to valuable connections and insights into current trends.
- Seek Internships: Gaining practical experience while building your resume is crucial. Internships provide a glimpse into the realities of your chosen field.
- Join Professional Organizations: Connecting with peers and mentors can offer support and guidance as you navigate your career path.

FAQ
Q: Can I pursue a career in finance with an MBA?
A: Absolutely! Many MBA programs offer specializations in finance, enabling graduates to pursue careers in investment banking, asset management, and other financial roles.
Q: Is an MBA or MFin better for entrepreneurship?
A: Both degrees can be beneficial for entrepreneurs. An MBA provides a broader business perspective, while an MFin focuses on specialized financial knowledge.
Q: What is the average salary for MBA and MFin graduates?
A: Typically, MBA graduates earn higher salaries than MFin graduates. However, both degrees offer strong earning potential, with median salaries for financial managers at approximately $134,000 and for financial analysts at about $81,000.
Q: How long does it take to complete an MBA or MFin program?
A: MBA programs generally take about two years to complete, while Master’s in Finance programs can often be finished in one to two years.
Conclusion
The decision between a Master’s in Finance vs MBA is a personal one, shaped by your individual career goals and aspirations. Both degrees offer valuable knowledge and skills that can open doors to rewarding career opportunities. Reflect on your interests, evaluate your financial situation, and consider the type of roles you envision for yourself in the future. Taking the time to research and understand these options will empower you to make an informed decision that aligns with your professional ambitions. Your future is bright, and the right degree can be a powerful investment in your career success.







Leave a Reply